In this blog post, I will give an overview of the role of Azure API Management in a microservices architecture, and how it can help manage, secure, and route requests to multiple microservices.
What is Azure API Management?
Azure API Management is a fully managed service responsible for managing, publishing, securing, and analyzing APIs in your environment. It also adds the benefits provided by Azure in the way of security and easy scalability features.
API Management acts as a facade or gatekeeper for your backend services and APIs. It sits between your applications and your API’s, providing a single point of entry and controlling traffic between them.
Azure API Management in a Microservices Architecture
In a microservices architecture, each service is a separate, independent unit that communicates with others through APIs. Each microservice runs its own process and allows for independent deployment and scaling capabilities which can be beneficial to your applications agility and resilience. Azure API Management can play a crucial role in such an architecture via the following benefits:
- Unified API Gateway: Azure API Management provides a unified API gateway for all your microservices, regardless of where they are hosted. This simplifies the client-side communication, as they only need to know about the API gateway, not the individual microservices.
This is why I personally find API Management so useful. Applications do not need to store information about hundreds of different API’s, such as the individual URLs and individual authentication requirements; they only need to know about and be authenticated to the API gateway, not the individual microservices. - Security: Azure API Management offers robust security and authentication features to protect your APIs. It supports multiple authentication mechanisms, including OAuth 2.0, OpenID Connect, and mutual certificate authentication. It also allows you to set up policies for rate limiting and quota enforcement to prevent abuse.
Another great feature of API Management is that it allows easy set up of a System-Assigned Managed identity which allows you to securely use useful side-car resources with Apim such as Key Vault and Storage Accounts. A great use case for this is the use of Key Vault Secret references in Apim Named Values. A guide on how to use this can be found here. - Monitoring and Analytics
With Azure API Management, you gain access to detailed analytics about the usage and performance of your APIs. This can help you identify trends, detect anomalies, and make informed decisions about scaling.
By integrating your Function Apps and API Management APIs with tools such as Azure Application Insights you can get a end to end overview of transactions occurring within your application which can greatly aid in debugging your APIs when issues occur.
I am planning on writing a blog post on setting up monitoring and dashboards for API Management soon so stay tuned. - Backend Management
Azure API Management abstracts the backend services, providing a layer of insulation between your API and backend. This allows you to modify or switch your backend services without impacting the client. It also enables you to manage backend services from different vendors, written in different programming languages, and hosted in different environments, all from a single place.
Integrating Azure API Management with Azure Functions
Pre-requisites:
– An Azure API Management Instance
– An Azure Function App with HTTP trigger
- Navigate to your API Management instance, select APIs from the left-hand menu, and click on Add API. Select Function App for the API type.

- In the screen that opens, select Browse. This will take you to a page where you can select your Function App.
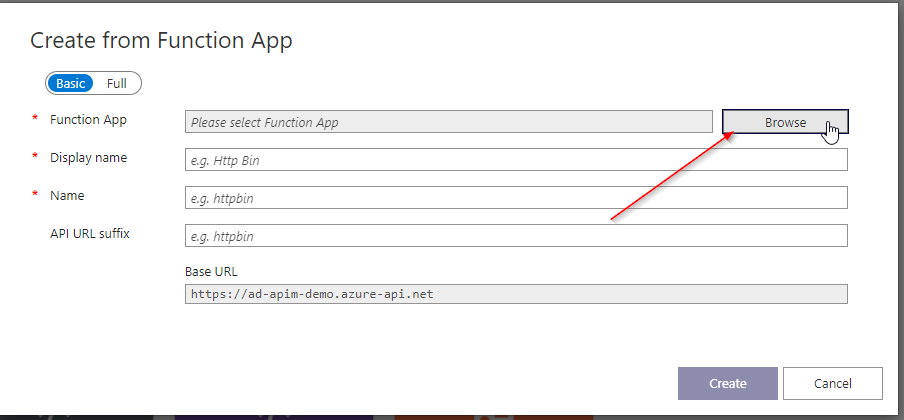
- In the next page, select the Function App that you wish to add to API Management.

Note: If you don’t see your Function App here, there may be some filtering that is going on that is stopping it from showing up here. Ensure you have Reader access to your Function App. If your Function App is in a different subscription to your API Management instance, ensure that your Subscription Filter is set to All Subscriptions in your portal settings.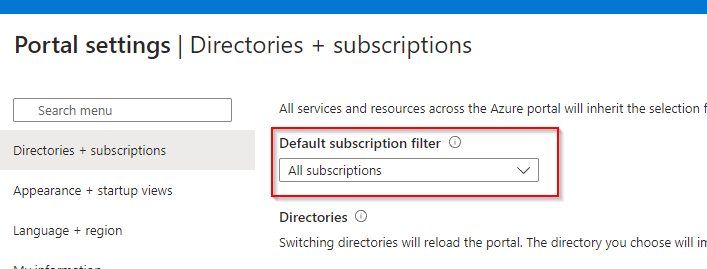
4. You should now see your new Function App linked API in your APIs list. You can test this new API by clicking on the Test tab and sending a new API request.
Integrating using Azure Bicep
Eventually you will want to set all this up via Infrastructure as Code and use it in your automated deployment pipelines. Below is a simple example on how to create an Azure Function App API in API Management using bicep.
resource api 'Microsoft.ApiManagement/service/apis@2020-06-01-preview' = {
name: '${apiManagement.name}/myApi'
properties: {
// api properties
}
}
resource operation 'Microsoft.ApiManagement/service/apis/operations@2020-06-01-preview' = {
name: '${api.name}/myOperation'
properties: {
// operation properties
urlTemplate: '/myFunction'
method: 'GET'
backendService: {
id: functionApp.properties.defaultHostName
url: 'https://myFunctionApp.azurewebsites.net/api/myFunction'
}
}
}In conclusion, Azure API Management and Azure Functions provide a robust and scalable solution for managing and integrating microservices. Azure API Management offers a unified gateway for all your microservices, abstracting the backend and providing features like rate limiting, security, and analytics.
Azure Functions allows you to run event-driven code without managing infrastructure, making it an ideal partner for API Management. The integration of these two services simplifies the architecture, enhances scalability, and improves the overall efficiency of your microservices ecosystem.
Whether you’re just starting your journey into microservices or looking to optimize your existing architecture, the combination of Azure API Management and Azure Functions is a powerful tool to have in your arsenal.
Leave a comment